Dental ABC
Are you ready to teach your child something new and informative that will make them sound super intelligent and wise? Presenting A-Z of Dental Terms that you can teach your children from the very beginning. Wanting to make your child a doctor- Start by teaching them this Dental ABC.
A — Abscess
Abscess - A pus-filled, inflamed area around a tooth.
A - Abscess
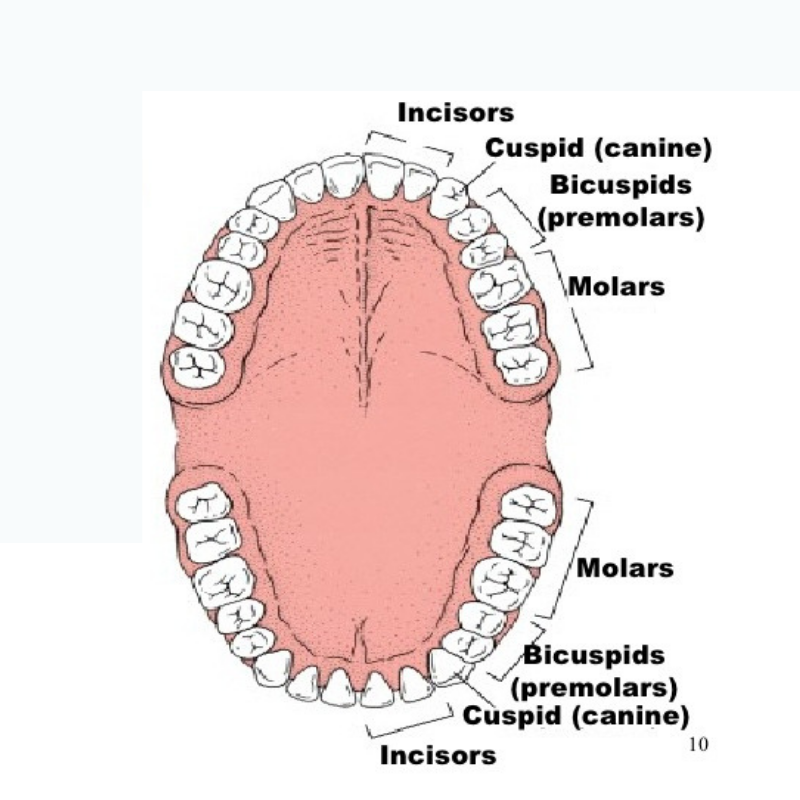
B — Bicuspid
Bicuspid - Also called premolars, bicuspid is an adult type of tooth located between the front teeth (incisors and canines) and the back teeth (molars). These teeth are used for crushing and mashing food, with two on the top and two on the bottom of each side of the mouth.
B- Bonding - Process that first etches the tooth's enamel, and then uses resin to attach tooth-colored fillings or veneers to a tooth.
B - Bridge - Non removable replacement for one or more missing teeth, anchored by teeth on either side of the gap. Bridges restore chewing ability and prevent neighboring teeth from shifting, which can result in a poor bite and gum disease.
B - Bruxism - Habitual, unconscious clenching of the jaw and/or grinding of the teeth. Approximately one in four adults grinds their teeth, usually while asleep or under stress. This problem can cause headaches and tooth damage.
C — CARIES
C- Caries - A word that means "rottenness" in Latin, this is the gradual decay and disintegration of a tooth. The decay can affect the tooth's soft or bony tissues.
C — Calculus - Hardened or calcified plaque that sticks to the teeth and causes decay and gum disease. It requires scaling by a dentist or dental hygienist to remove.
C — Cavity - Hole or weak area in a tooth, caused by tooth decay (caries).
C — Composites - Tooth-colored materials used as fillings or bonding to restore teeth. Most are made of resin, a plastic mixture filled with ground-up "glass" particles (silicon dioxide).
C — Crown ("cap") - Part of the tooth that's visible above the gum, or the artificial substitute for it. A restorative crown covers the top part of a tooth that is severely damaged or weakened by decay. A crown is made of metal, resin, porcelain, or porcelain-covered metal, and cemented onto the tooth.
C — Cuspid - Pointy tooth, also called a canine (for their resemblance to dogs' fangs), located on either side of the incisors, the four teeth in the very front of the mouth. Adults have four cuspids that are used to tear food, two on the top and two on the bottom.
D — Dentin
Dentin - Middle layer of the tooth, below the enamel and surrounding the pulp.
D — Dry socket - Painful condition following a tooth extraction caused by a blood clot that does not properly fill the empty socket, leaving the bone underneath exposed to air and food.
E - Enamel
Enamel — A hard, white outer layer of a tooth. Enamel is the hardest substance in the body.
Endodontist — A dentist who specializes in endodontics, or the treatment of the root and nerve system in teeth.
F — FLUORIDE
Fluoride - Chemical compound added to toothpaste and drinking water that helps strengthen and repair the surface of teeth and prevent cavities.
G — GINGIVITIS
Gingivitis - Inflammation of the gums often caused by a buildup of food particles and plaque (a sticky film containing bacteria) on and around the teeth.
G — Gum disease - An illnesses that inflame and, if untreated, can destroy the gum tissues and bones that support and anchor teeth.
H — HALITOSIS
Halitosis - Bad breath, which can be caused or worsened by a dry mouth, poor dental hygiene, bacteria mixed with putrefying food particles in the mouth, sinus problems, or other conditions.
I — INCISOR
Incisor - Type of tooth located at the front of the mouth. Adults have eight of these flat teeth (four on the top and four on the bottom), and they are used primarily to bite and cut food.
I — Impacted tooth - Any tooth (but especially a wisdom tooth) that cannot break through the gum into normal position because it is growing against or blocked by bone, soft tissue, or another tooth.
I — Implant - Material inserted or grafted into tissue.
J — Jaw
Jaw — A common name for either the maxilla or the mandible.
M — MOLAR
Molar - Type of tooth located in the back of the mouth behind the bicuspids. Adults have eight molars (12 if they still have their wisdom teeth), which have a flat bumpy surface good for the toughest chewing jobs.
M — Malocclusion - A condition in which the upper and lower teeth do not fit together properly. An overbite is a common example of a malocclusion.
M — Mucin - Protein found in the saliva that mixes with sugars to form bacterial plaque.
0 — ORTHODONTIST
Orthodontist - A dentist who specializes in orthodontics, or the correction of misaligned teeth and jaws with braces, retainers, or other dental appliances.
P - PEDODONTIST
Pedodontist - A dentist who specializes in pedodontics, or dentistry for children.
P — Periodontist - A dentist who specializes in periodontics, or the treatment of the gums, soft tissues, and bones that support the teeth.
P — Periodontal Disease - Any gum disease (such as periodontitis or gingivitis) that, if untreated, inflames and eventually destroys the bone and tissues that support and anchor the teeth.
P — Plaque - Sticky, colorless film containing bacteria that forms on teeth and causes tooth decay and gum disease if it is not removed by brushing and flossing.
P — Prosthodontist - A dentist who specializes in prosthodontics, or the restoration and replacement of missing teeth with artificial materials.
P — Pulp- Innermost layer of the tooth, below the enamel and dentin, which contains the nerves and blood vessels.
P — Pulpitis - Inflammation of the pulp (the tooth's innermost layer) caused by a cavity or other trauma, and often signaled by a painful toothache.
R- RADIOGRAPH
Radiograph - X-ray
R— Root canal (endodontic treatment) - Procedure in which the diseased nerve (also called the pulp or inside core) of a heavily decayed or damaged tooth is removed and the central pulp space of the tooth is filled and sealed with dental cement.
T — TARTAR
Tartar — Hard deposit, or calcified bacterial plaque, which sticks to the teeth and causes decay. See Calculus.
W — WISDOM TEETH
Wisdom teeth - Back teeth, also called third molars, that usually come in between the ages of 15 to 25. In ancient times, humans needed these teeth to chew and grind raw food, but today many people have them removed because they are hard to clean, which in turn can lead to infection, or because there is no room in the jaw for these teeth to grow in straight.
Visual of Impacted Wisdom Teeth